一、多线程爬虫
实例:
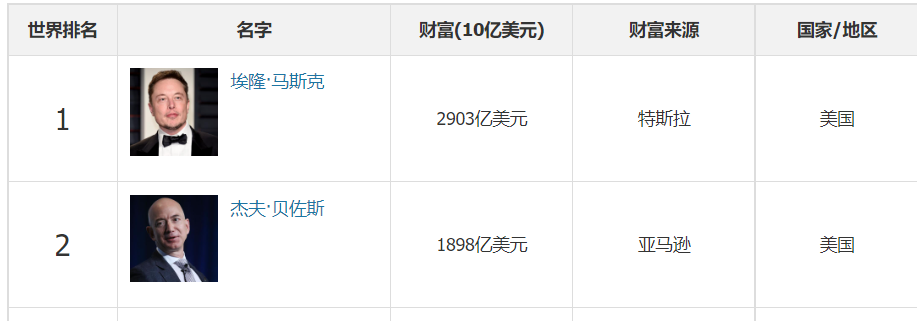
爬取福布斯富豪榜,并保存到csv文件。
这里因涉及隐私问题不在代码中展示怕爬取网站,可以参考基本框架方法。
# 如何提取单页面的数据
# 上线程池,多个页面同时抓取
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import requests
from lxml import etree
import csv
f = open('./爬虫学习/多线程/富豪榜.csv','w',encoding='utf-8')
csvwriter = csv.writer(f)
def download_one_page(url):
head = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'}
resp = requests.get(url,headers=head)
resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
html = etree.HTML(resp.text)
trs = html.xpath('//table/tbody/tr')
for tr in trs[1:]:
txt1 = tr.xpath('./td[1]/text()')
txt2 = tr.xpath('./td[2]/a/p/text()')
txt3 = tr.xpath('./td[3]/text()')
txt4 = tr.xpath('./td[4]/text()')
txt5 = tr.xpath('./td[5]/a/text()')
data = txt1 + txt2 + txt3 + txt4 + txt5
csvwriter.writerow(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
csvwriter.writerow(['世界排名','名字','财富','财富来源','国家/地区'])
# 创建线程池
with ThreadPoolExecutor(50) as t:
for i in range(1,16):
t.submit(download_one_page,f'https://www.phb123.com/renwu/fuhao/shishi_{i}.html')
print('爬取完成')
文件前几行内容:

二、异步爬虫
这里用到异步网络请求模块 (aiohttp),随便爬取网上找的三张图片。
注意: s = aiohttp.ClientSession() <=> requests s.get() <=> requests.get() s.post() <=> requests.post()
import asyncio
import aiohttp
urls = ['https://file07.16sucai.com/2020/0813/d5197dcfd1c6cd422fb1da90ece3700c.jpg',
'https://file07.16sucai.com/2020/0915/6760ca48e3f66b46e4ee723f3818f564.jpg',
'https://file07.16sucai.com/2020/0903/9d9455af6c295e0af0fa2799a292d3b6.jpg'
]
async def aiodownload(url):
name = url.rsplit('/',1)[1]
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: #用with有上下文管理,使用完之后自动关闭
async with session.get(url) as resp: #requests.get()
#请求回来,写入文件,可以学习aiofiles,创建文件也异步
with open(name,mode='wb') as f:
f.write(await resp.content.read()) #读取内容是异步的,需要await挂起
#resp.content.read() #这是读取图片==resp.content,读取文本用resp.text(),原来resp.text
#发送请求
#得到图片
#保存文件
async def main():
tasks = []
for url in urls:
tasks.append(asyncio.create_task(aiodownload(url)))
await asyncio.wait(tasks)
if __name__ == '__main__':
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
print('完成')
#asyncio.run(main())不行,因为async定义的函数会返回一个 coroutine 协程对象,
# 关于这个对象必须要注册到事件循环中去才可以执行,而我们原来的asyncio.run(main())会自动关闭循环
# (就是前面提到的Loop event),并且调用_ProactorBasePipeTransport.__del__报错, 而asyncio.run_until_complete()不会.
注意: asyncio.get_event_loop() 用来获取当前正在运行的循环实例,然后传入run_until_complete()执行。具体参考 解决我们不在主线程上并且没有通过其他方式实例化运行循环,引发的RuntimeError问题。